UNDERSTANDING SOLAR NET-METERING
Net metering is a billing mechanism enabling owners of solar energy systems to feed the
surplus electricity they generate back into the grid.
In exchange, they receive credits that offset their electricity consumption. It ensures that
excess energy produced by their solar panels contributes to the overall energy supply rather
than going unused.
HOW NET-METERING WORKS?
Solar Energy Production: Solar panels generate more electricity during the
daytime, often
generating more power than the household consumes.
Energy Export: The surplus energy is sent to the grid, and the meter runs
backward, crediting the
homeowner for the excess power.
Energy Import: At night or during cloudy days when solar panels produce
less or no energy,
homeowners draw electricity from the grid, using the credits accumulated.
BENEFITS OF NET-METERING
COST SAVINGS:
Net metering provides homeowners with a notable opportunity to lower
their electricity expenses.
By earning credits for surplus power generated by their solar panels,
homeowners can offset their electricity consumption at night when their
panels are not producing energy.
Environmental Impact:
Net metering promotes the adoption of solar energy, which can reduce
dependence on fossil fuels, lowering greenhouse gas emissions and the
global carbon footprint.
According to the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), solar power
has the potential to offset up to 100 million metric tons of CO2 annually by
2030.
GRID STABILITY:
Net metering in solar increases grid stability by offering a decentralized
power source.
As more homes generate solar energy, it decreases reliance on centralized
power plants, resulting in fewer outages and a more robust net metering
system in solar power infrastructure.
Incentivizing Renewable Energy Adoption:
The financial incentives provided by net metering encourage more
homeowners to install solar panels.
This increased adoption drives down the cost of solar technology through
economies of scale, making renewable energy more accessible to a broader
population.
TYPES OF NET-METERING
STANDARD NET-METERING:
Standard Net Metering, the most prevalent form of net metering, allows
homeowners to offset their electricity consumption with energy credits earned
from excess power generation on a one-to-one basis.
It is a simple and advantageous approach for homeowners with consistent and
predictable energy usage patterns.
TIME-OF-USE (TOU) NET-METERING:
In Time-of-Use (TOU) net metering, the worth of energy credits fluctuates based
on the time of day.
Electricity generated during peak hours, when demand and prices are highest,
earns more valuable credits.
This approach can maximize cost savings for individuals who want to adjust their
energy consumption patterns accordingly.
VIRTUAL NET-METERING:
Virtual net metering enables multiple users, such as tenants in an apartment
building, to benefit from a shared solar energy system.
Credits generated by the solar panels are allocated among all participants, making
net metering in solar accessible to individuals who may not have suitable roofs for
individual installations.
PRE-REQUISITES OF NET-METERING INSTALLATION
The process of installing net metering involves many steps. Here you will
get the step-by-step process of net metering installation:
ASSESS ELIGIBILITY:
Before diving into the net metering process, it is essential to determine if you
are
eligible for net metering.
The eligibility criteria may vary depending on the country or state where you
reside.
Generally, residential, commercial, and industrial customers with on-grid solar
systems are eligible.
Some factors considered for eligibility may include the size of the solar system,
local
regulations, and the capacity of the electricity grid.
CONTACT YOUR UTILITY PROVIDER:
Once you have confirmed your eligibility, the next step is to get in touch with
your
utility provider.
Inform them about your intention to install a solar system and inquire about their
net
metering program.
They will provide you with the necessary information and guidance on the specific
requirements and procedures to follow.
INSTALL THE SOLAR SYSTEM:
To participate in net metering, you need to install a solar PV system on your
property.
It is recommended to engage with a reputable solar installer who can assess your
energy needs, determine the optimal system size, and install solar panels in
compliance with local regulations and safety standards.
The installer will also assist you in obtaining the necessary permits and
approvals.
PROCESS OF NET-METERING INSTALLATION
NET-METERING AGREEMENT:
Before the net metering arrangement begins, you will need
to sign a net metering agreement with your utility provider.
This agreement outlines the terms and conditions of the
net metering program, including the credit calculation
methodology, billing procedures, contract duration, and
any additional requirements or restrictions.
ENERGY PRODUCTION AND BILLING:
With the net metering system in place, your solar system
will start generating electricity.
The excess energy produced by your system will flow into
the grid, and you will receive credits for it.
These credits will be deducted from your future electricity
bills, offsetting the cost of electricity you consume from
the grid during periods of low solar production.
DETAILED PROCESS TO INSTALL NET-METERING SYSTEM IN
INDIA
Applicants need to send an application to the SDO to seek permission to install a
rooftop solar panel.
Applicants need to collect the approval receipt from the sub-divisional
officer.
SDO completes the site verification within three days after application and
approval.
After the site inspection, SDO approves within 15 days from application
submission.
Consumer and SDO sign a net metering agreement within three days of filling up the
net metering form.
After installing the solar system, consumers shall submit a solar system
certificate, property papers, installation certificate, and fees.
In the end, a JE visits the site to inspect the solar panel installation. If all
the rules are met, the JE gives permission to install a metering energy
system.
NET-METERING APPROVAL CHECKLIST
Applicants need to follow the given checklist to concisely monitor their solar metering
energy application:
STAGE 1:
Submit duly signed application.
Provide roof right and occupancy proof.
Applicant’s signature ID proof.
Copy of recently paid electric bill.
Applicants who are tenants or co-owner of property must submit the NOC of the
owner or co-owners.
Undertaking that is signed by a registered customer and attested by a notary
public.
Applicant’s photograph.
STAGE 2:
Submit a registration form that is duly attested by the registered
consumer.
Subsidy sanction request letter.
EPC agreement for CAPEX and PPA for RESCO.
Receiving letter for metering energy application.
Colored photo of the site with clear stamping of date and time before solar panel
installation.
Project report as per the Annexure-D format of tender document.
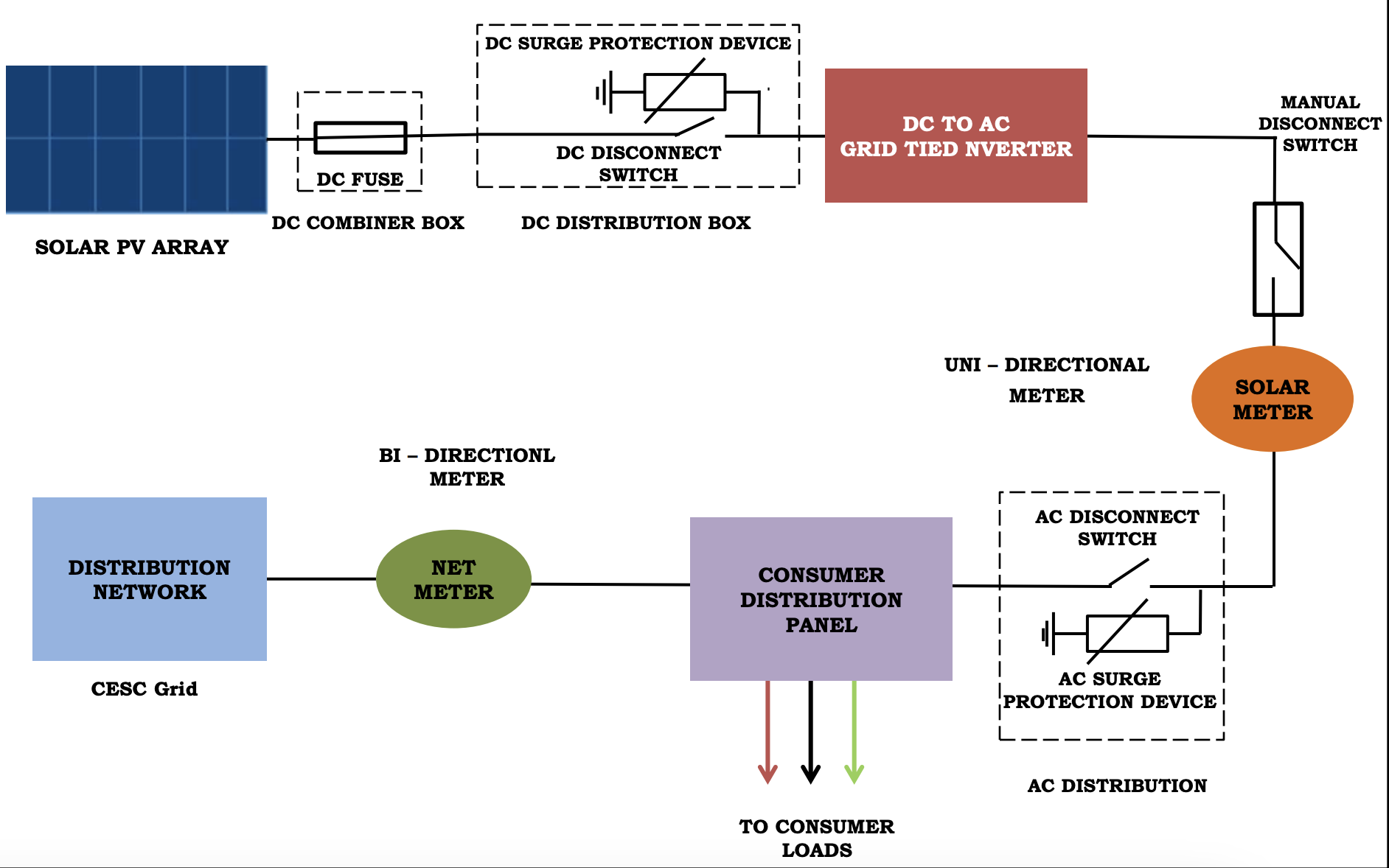
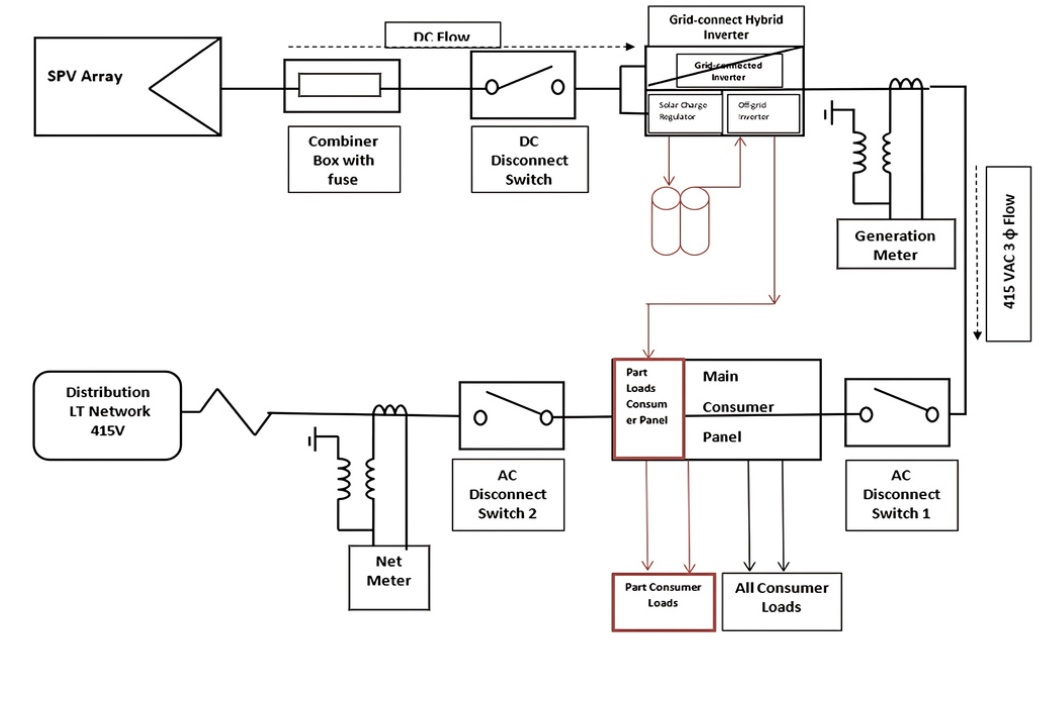
Single lined diagram of the solar plant.
System certification for the PV module inverters.
Specifications of inverter and solar PV module.
Non-judicial stamp paper agreement for metering energy connection